130 lines
4.4 KiB
Markdown
130 lines
4.4 KiB
Markdown
# Kotlin 에서 ArgumentCaptor<T> 를 이용한 테스트 작성시 주의할 점
|
|
|
|
Kotlin 프로젝트에서 `ArgumentCaptor<T>`를 이용한 테스트를 작성하던중, 마주친 문제가 있어 정리해둔다.
|
|
|
|
## `org.mokito.ArgumentCaptor<T>`
|
|
|
|
org.mokito에 포함되어 있는 `ArgumentCaptor<T>` 를 사용하면 함수 호출시 인자로 넘기는 값들에 대해서 검사를 진행할 수 있다.
|
|
|
|
## 문제 상황
|
|
|
|
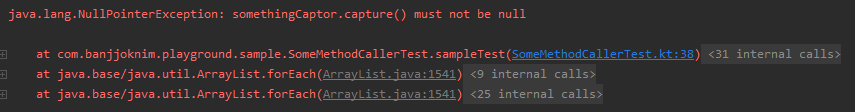
`ArgumentCaptor<T>` 를 이용한 테스트를 작성하던 도중 아래와 같이 에러를 뿜으며 테스트가 제대로 수행되지 않았다. 이유가 뭘까?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 예제 코드
|
|
|
|
아래는 위 상황이 발생한, 실패하는 예제 코드다.
|
|
|
|
```kotlin
|
|
class SomeMethodCaller {
|
|
fun someMethod(something: Something) {
|
|
// do something
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
```kotlin
|
|
data class Something(val hello: String, val world: String)
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
```kotlin
|
|
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension::class) // if use JUnit5, use this. or another...
|
|
//@SpringBootTest
|
|
class SomeMethodCallerTest {
|
|
|
|
@Mock
|
|
val someMethodCaller: SomeMethodCaller = SomeMethodCaller()
|
|
|
|
// @MockBean // if use @SpringBootTest, can use this
|
|
// lateinit var someMethodCaller: SomeMethodCaller
|
|
|
|
@Captor
|
|
lateinit var somethingCaptor: ArgumentCaptor<Something>
|
|
|
|
@Test
|
|
fun sampleTest() {
|
|
// given
|
|
val something = Something("hello", "world")
|
|
|
|
// when
|
|
someMethodCaller.someMethod(something)
|
|
|
|
// then
|
|
then(someMethodCaller).should().someMethod(somethingCaptor.capture()) // example 1.
|
|
verify(someMethodCaller).someMethod(somethingCaptor.capture()) // example 2.
|
|
assertThat(somethingCaptor.value).isEqualTo(something)
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Java vs Kotlin
|
|
|
|
가장 먼저, Java와 Kotlin 의 타입 시스템을 이해할 필요가 있다.
|
|
|
|
Java에서는 기본적으로 모든 참조 타입은 null을 허용하고 있지만, Kotlin에서는 아예 분리되어 있다.
|
|
|
|
```kotlin
|
|
// Java
|
|
String word = null; // ok
|
|
|
|
// Kotlin
|
|
var word: String? = null // ok
|
|
var word: String = null // Null can not be a value of a non-null type String
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Java의 class는 참조 타입이므로 null이 허용되는 타입, 즉 Kotlin에서는 nullable 타입이라고 볼 수 있다.
|
|
|
|
`org.mokito.ArgumentCaptor<T>` 는 Java 기반 라이브러리이다.
|
|
|
|
따라서 Kotlin에서 사용하기 위해서는 Java에서의 null 이 허용되는 nullable 타입을 Kotlin에서의 non-null 타입으로 변경해주어야 한다(반대의 경우도 마찬가지다. 본 글의 상황에서는
|
|
nullable을 non-null 타입으로 변경해주어야 했다. 즉, 호출자가 받는 인자의 타입에 맞게 변경해주어야 한다).
|
|
|
|
## 해결
|
|
|
|
따라서 아래와 같이 nullable 타입으로 선언된 인자를 non-null로 변경해주는 도우미 함수를 작성한 뒤 사용하면 참조 타입에 대해서도 ArgumentCaptor<T> 를 사용할 수 있다.
|
|
|
|
```kotlin
|
|
private fun <T> capture(argumentCaptor: ArgumentCaptor<T>): T = argumentCaptor.capture()
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
아래는 문제를 해결한 전체 예제 코드다. 크게 달라진 건 없으며, `capture()` 함수가 추가되고 해당 함수를 사용하는 것만 달라졌다.
|
|
|
|
```kotlin
|
|
private fun <T> capture(argumentCaptor: ArgumentCaptor<T>): T = argumentCaptor.capture()
|
|
|
|
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension::class) // if use JUnit5, use this. or another...
|
|
//@SpringBootTest
|
|
class SomeMethodCallerTest {
|
|
|
|
@Mock
|
|
val someMethodCaller: SomeMethodCaller = SomeMethodCaller()
|
|
|
|
// @MockBean // if use @SpringBootTest, can use this
|
|
// lateinit var someMethodCaller: SomeMethodCaller
|
|
|
|
@Captor
|
|
lateinit var somethingCaptor: ArgumentCaptor<Something>
|
|
|
|
@Test
|
|
fun sampleTest() {
|
|
// given
|
|
val something = Something("hello", "world")
|
|
|
|
// when
|
|
someMethodCaller.someMethod(something)
|
|
|
|
// then
|
|
then(someMethodCaller).should().someMethod(capture(somethingCaptor)) // example 1.
|
|
verify(someMethodCaller).someMethod(capture(somethingCaptor)) // example 2.
|
|
assertThat(somethingCaptor.value).isEqualTo(something)
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
위 코드로 테스트를 진행하면 성공하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
|
|
|
|
## 참고자료
|
|
|
|
- [kotlin and ArgumentCaptor](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/34773958/kotlin-and-argumentcaptor-illegalstateexception)
|
|
- [Mockito-Kotlin Sample로 자세히 알아보기](https://beomseok95.tistory.com/m/297) |