237 lines
8.9 KiB
Markdown
237 lines
8.9 KiB
Markdown
# 순수 JDBC
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## 환경 설정
|
|
|
|
### build.gradle 파일에 jdbc, h2 데이터베이스 관련 라이브러리 추가
|
|
```
|
|
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-jdbc'
|
|
runtimeOnly 'com.h2database:h2'
|
|
```
|
|
- 자바는 기본적으로 `DB`와 연결하려면 `jdbc` 드라이버(여기서는 `'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-jdbc'`)가 반드시 있어야 하며, 이를 통해 연동한다.
|
|
|
|
### 스프링 부트 데이터베이스 연결 설정 추가(`resources/application.properties`에 추가)
|
|
```
|
|
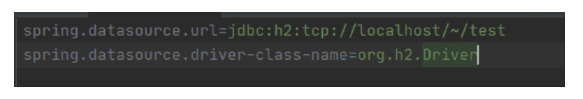
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost/~/test
|
|
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.h2.Driver
|
|
spring.datasource.username=sa
|
|
```
|
|
- `DB`와 연결될 때 데이터베이스가 제공하는 클라이언트(여기서는 `'com.h2database:h2'`)가 필요하다.
|
|
- `DB`와 연결하려면 접속정보를 넣어줘야 한다(`application.properties`에 기재).
|
|
- 이렇게 기재하면 스프링이 데이터베이스와 연결하는 작업을 다 해준다. 이제 갖다 쓰기만 하면된다.
|
|
|
|
> **주의!**
|
|
>
|
|
>스프링부트 2.4부터는 spring.datasource.username=sa 를 꼭 추가해주어야 한다. 그렇지 않으면 Wrong user name or password 오류가 발생한다. 참고로 다음과 같이 마지막에 공백이 들어가면 같은 오류가 발생한다. spring.datasource.username=sa 공백 주의, 공백은 모두 제거해야 한다.
|
|
|
|
> **참고**
|
|
>
|
|
> 인텔리J 커뮤니티(무료) 버전의 경우 application.properties 파일의 왼쪽이 다음 그림과 같이 회색으로 나온다. 엔터프라이즈(유료) 버전에서 제공하는 스프링의 소스 코드를 연결해주는 편의 기능이 빠진 것인데, 실제 동작하는데는 아무런 문제가 없다.
|
|
>
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## javax.sql.DataSource
|
|
- `DB`와 연동하기 위해 필요하다.
|
|
- 스프링한테 주입받아야 한다.
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## Jdbc 리포지토리 구현
|
|
```java
|
|
public class JdbcMemberRepository implements MemberRepository {
|
|
private final DataSource dataSource;
|
|
|
|
public JdbcMemberRepository(DataSource dataSource) {
|
|
this.dataSource = dataSource;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
public Member save(Member member) {
|
|
String sql = "insert into member(name) values(?)";
|
|
Connection conn = null;
|
|
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
|
|
ResultSet rs = null;
|
|
try {
|
|
conn = getConnection();
|
|
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql,
|
|
Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
|
|
pstmt.setString(1, member.getName());
|
|
pstmt.executeUpdate();
|
|
rs = pstmt.getGeneratedKeys();
|
|
if (rs.next()) {
|
|
member.setId(rs.getLong(1));
|
|
} else {
|
|
throw new SQLException("id 조회 실패");
|
|
}
|
|
return member;
|
|
} catch (Exception e) {
|
|
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
|
|
} finally {
|
|
close(conn, pstmt, rs);
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
public Optional<Member> findById(Long id) {
|
|
String sql = "select * from member where id = ?";
|
|
Connection conn = null;
|
|
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
|
|
ResultSet rs = null;
|
|
try {
|
|
conn = getConnection();
|
|
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
|
|
pstmt.setLong(1, id);
|
|
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
|
|
if (rs.next()) {
|
|
Member member = new Member();
|
|
member.setId(rs.getLong("id"));
|
|
member.setName(rs.getString("name"));
|
|
return Optional.of(member);
|
|
} else {
|
|
return Optional.empty();
|
|
}
|
|
} catch (Exception e) {
|
|
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
|
|
} finally {
|
|
close(conn, pstmt, rs);
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
public List<Member> findAll() {
|
|
String sql = "select * from member";
|
|
Connection conn = null;
|
|
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
|
|
ResultSet rs = null;
|
|
try {
|
|
conn = getConnection();
|
|
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
|
|
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
|
|
List<Member> members = new ArrayList<>();
|
|
while (rs.next()) {
|
|
Member member = new Member();
|
|
member.setId(rs.getLong("id"));
|
|
member.setName(rs.getString("name"));
|
|
members.add(member);
|
|
}
|
|
return members;
|
|
} catch (Exception e) {
|
|
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
|
|
} finally {
|
|
close(conn, pstmt, rs);
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
public Optional<Member> findByName(String name) {
|
|
String sql = "select * from member where name = ?";
|
|
Connection conn = null;
|
|
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
|
|
ResultSet rs = null;
|
|
try {
|
|
conn = getConnection();
|
|
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
|
|
pstmt.setString(1, name);
|
|
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
|
|
if (rs.next()) {
|
|
Member member = new Member();
|
|
member.setId(rs.getLong("id"));
|
|
member.setName(rs.getString("name"));
|
|
return Optional.of(member);
|
|
}
|
|
return Optional.empty();
|
|
} catch (Exception e) {
|
|
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
|
|
} finally {
|
|
close(conn, pstmt, rs);
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
private Connection getConnection() {
|
|
return DataSourceUtils.getConnection(dataSource);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
private void close(Connection conn, PreparedStatement pstmt, ResultSet rs) {
|
|
try {
|
|
if (rs != null) {
|
|
rs.close();
|
|
}
|
|
} catch (SQLException e) {
|
|
e.printStackTrace();
|
|
}
|
|
try {
|
|
if (pstmt != null) {
|
|
pstmt.close();
|
|
}
|
|
} catch (SQLException e) {
|
|
e.printStackTrace();
|
|
}
|
|
try {
|
|
if (conn != null) {
|
|
close(conn);
|
|
}
|
|
} catch (SQLException e) {
|
|
e.printStackTrace();
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
private void close(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
|
|
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(conn, dataSource);
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
>**주의!**
|
|
>
|
|
>이렇게 JDBC API로 직접 코딩하는 것은 20년 전 이야기이다. 따라서 고대 개발자들이 이렇게 고생하고 살았구나 생각하고, 정신건강을 위해 참고만 하고 넘어가자.
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## 스프링 프레임워크에서 데이터베이스 Connection을 사용할 때 주의할 점
|
|
- 반드시 `DataSourceUtils.getConnection()`을 통해서 `Connection`을 획득해야 한다.
|
|
- 트랜잭션이 걸리거나 했을 때 똑같은 데이터베이스 커넥션을 유지해야 하는데, 위의 방법으로 해야 유지시켜준다.
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
private Connection getConnection() {
|
|
return DataSourceUtils.getConnection(dataSource);
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
- 닫을 때도 `DataSourceUtils`를 이용해서 릴리즈 해줘야 한다.
|
|
|
|
```java
|
|
private void close(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
|
|
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(conn, dataSource);
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## 추가 설명
|
|
|
|
- 스프링 부트는 데이터베이스 설정 파일를 보고 스프링 자체적으로 빈(데이터베이스와 연결할 수 있는 정보가 담긴 `DataSource`)도 생성해준다.
|
|
|
|
- `DataSource`는 데이터베이스 커넥션을 획득할 때 사용하는 객체다. 스프링 부트는 데이터베이스 커넥션 정보를 바탕으로 DataSource를 생성하고 스프링 빈으로 만들어둔다. 그래서 DI를 받을 수 있다.
|
|
|
|
- `다형성을 활용한다` : 인터페이스를 두고 구현체를 바꿔끼우기 하는 것.
|
|
- 스프링은 이를 편리하게 할 수 있도록 스프링 컨테이너가 지원해준다.
|
|
- `DI` 덕분에 다형성을 편리하게 활용할 수 있다.
|
|
|
|
- `어셈블리(조립)` : 기존의 코드는 하나도 손대지 않고 애플리케이션을 설정하는 것, 조립하는 코드만 약간 수정하면 실제 애플리케이션에 관련된 코드는 하나도 손대지 않아도 된다.
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
## 구현 클래스 추가 이미지
|
|
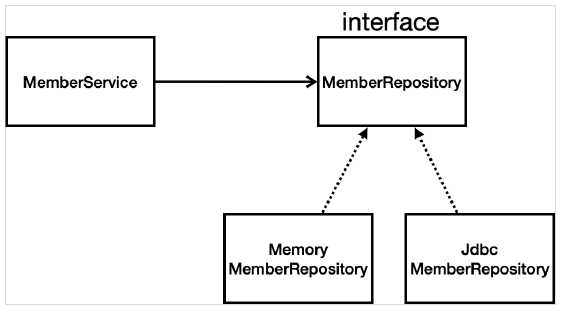
|
|
|
|
## 스프링 설정 이미지
|
|
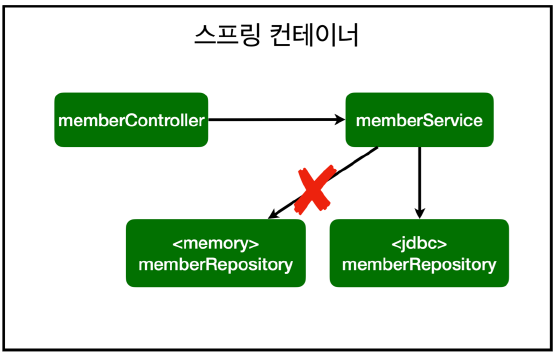
|
|
|
|
- 개방-폐쇄 원칙(OCP, Open-Closed Principle)
|
|
- 확장에는 열려있고, 수정, 변경에는 닫혀있다.
|
|
- 스프링의 DI (Dependencies Injection)을 사용하면 기존 코드를 전혀 손대지 않고, 설정만으로 **구현 클래스를 변경**할 수 있다.
|
|
- 회원을 등록하고 DB에 결과가 잘 입력되는지 확인하자.
|
|
- 데이터를 DB에 저장하므로 스프링 서버를 다시 실행해도 데이터가 안전하게 저장된다.
|
|
|
|
--- |